Comparison of Routing Protocols in-terms of Packet Transfer Having IPV6 Address Using Packet Tracer-Juniper Publishers
Juniper publishers-Open access journal of Engineering Technology
Abstract
In the network the transmission of data is based on
the protocols which play a vital role in terms of packet transfer. A
routing protocol is a protocol which is responsible to determine how
routers communicate with each other and forward the packets through
optimal path to travel from source node to destination node. Each
routing protocols performs in different ways they have their own
architecture, route to follow sometimes even delays in packets. This
paper is basically the comparison of three different routing protocols
which are RIP, EIGRP, OSPF using the network simulator called Packet
Tracer having IPV6 as an address since IPv4 addressing space has almost
been exhausted many organization will soon be required to perform the
changeover to IPv6 which is more secure and a study analysis three
popular routing protocols; RIP, OSPF and EIGRP and the major differences
have been identified and discussed hence result show which protocols
works more efficiently and have faster.
Keywords: RIP; EIGRP; OSPF; IPV6; Packet TracerIntroduction
Background
In modern era of information technology,
communication networks are growing rapidly day by day. To provide
efficient routing in the network several routers take part in the
networks which not only forwards the information in the form of packets
but also keeps an eye on the data so that it remains in control manner.
Routing protocols specify how routers communicate with each other by
disseminating information. The router has prior knowledge about the
adjacent networks which can assist in selecting the routes between two
nodes [1].
Each routing protocols have their own algorithm and
have difference in performance basically Three typical types of routing
protocol are chosen as the simulation samples: RIP, OSPF and EIGRP. RIP
(Routing Information Protocol) is one of the oldest routing protocols
still in service. Hop count is the metric that RIP uses, and the hop
limit limits the network size that RIP can support. OSPF (Open Shortest
Path First) is the most widely used IOSPF is based on the Shortest Path
First (SPF) algorithm which is used to calculate the shortest path to
each node. EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) is Cisco’s
proprietary routing protocol based on Diffusing Update Algorithm.
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) were designed to
address the problem of limited address space by providing 128bits of
addressing space, providing 2128 IP addresses; a practically limitless
addressing space for new internet enabled devices to utilize IPv6 brings
a number of improvements over IPv4 in addition to increased addressing
space; IPv4 contains no securitymechanisms rather rely on the protocols
and reason to switch from IPV4 to IPV6 is higher number of nodes can be
connected and for the higher security mechanism.
In this paper we review the three different routing
protocols in times-stamp to deliver the packet from one node then
receive the message of delivery which simply show the time taken to
travel the packet from source to destination. And time taken for message
to travel is noted down, routing protocols are configuring separately
and study using graph which is done in the network simulator called
packet tracer which is the advance tools which provide the environment
to configure the protocols virtually and study the times-stamp for each
routing protocols.
Objective
The primary objective of this research paper is to
study the different routing protocols by using the network simulator
Packet Tracer and determine the transfer of packet from one node to
another node and study how these protocols perform individually. In
order to fulfill the primary objectives, secondary objectives of the
research paper are to study the protocols in detail and in network
simulator the nodes been configured with the IPV6 as an address which
means large number of nodes can be added but, in this research, paper
conducted with the configuration using two different networks. The
outcomes been generated in the table with respect to the sending and
receiving packets and message
from source to destination and from generated table the graph
been plotted with their respective data and conclude that which
routing protocols performs faster when the network model have
same configuration using different routing protocols.
Research questions
1. The time taken by the packet to travel from source to
destination and which route the packet travel?
2. Comparatively which routing protocols performs better?
The paper has been further divided into six sections. From
brief introduction to the final conclusion where section 3 to 3
show the brief introduction about the protocols as well the IP
address that conducted in the network model. Section 4 show the
simulation setup where the model been design and implement the
network with different routing protocols. Then finally methods in
next section.
Dynamic Routing Protocols
In computer networks, the routing protocol specifies how
routers communicate to select the routes for information or data
transfer for that, the routing algorithm is more important First,
the routing protocol informs or shares the information with their
associative neighbors and then throughout the network, in which
topology is determined [2]different types of dynamic routing
protocols are RIP, EIGRP, OSPF. Dynamic routing protocols provide
increased scalability over static alternatives and the ability to
automatically adjust to network topological changes such as a
failed component; rerouting traffic through alternative paths
automatically with minimal disruption[3].
Rip(Routing Information Protocol)
RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol in which distance
vector routing protocol is used for data/packet transmission. In
Routing Information protocol (RIP), the maximum number of Hop
is 15,as the route goes beyond 15 then the hos is unreachable
because it prevents routing loops from source to destination.
As comparing to other routing protocols RIP have the less limit
size and used for small network main advantage of RIP over
other protocols is that it uses UDP(user data program).Rip has
basically four timer which is update timer(default 30 seconds),
invalid timer(default 180 seconds), hold down timer(default 180
seconds), flush timer(default 240 seconds). the only issue in the
rip is that is performs slowly and for faster Rip in small network
RIPV2 is used which is RIP version2.
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
is a hybrid routing protocol. EIGRP saves all routes rather than
the best route to ensure the faster convergence. EIGRP keeps
neighboring routing tables and it only exchange information that
its neighbor would not contain. EIGRP is commonly used in large
networks, and it updates only when a topology changes but not
periodically unlike old Distance-Vector protocols such as RIP. The
fast convergence feature in EIGRP is due to the Diffusing Update
Algorithm (DUAL). The diffusing update algorithm is a routing
protocol used by EIGRP to calculate and create routing tables to
determine whether a path is looped or loop-free and it determine
the most efficient (least cost) route to a destination. It also allows
a router running EIGRP to find alternate paths without waiting on
updates from other routers [1].
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
OSPF is the most widely used routing protocol in large
enterprise networks. OSPF is based on link-state technology by
using shortest path first(SPF) algorithm which calculates the
shortest path among all the possible path. OSPF puts the possible
route in the topology map and select the best route to travel.which
will be the shortest path among all the possible route.Compare
to RIP, OSPF has no limitation due to hops (RIP has a limit of 15
hops so any network with more than 15 hops cannot be achieved
by RIP. OSPF can handle Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSM)
but RIP cannot. The most important is that OSPF converges
much faster than RIP due to its calculation algorithm. This might
not be significant in a small size network but in large enterprise
networks, this will be a time out[4-6].
IPV6
The new version of the IP protocol that was to be developed
required the following main objectives: extend the IP address
space, correct the defects of IPv4 standard and improve its
performance as much as possible, anticipate future needs,
and promote innovation by simplifying the implementation of
functional extensions to the protocol.First of all, IPv6 provides
a much larger address space than IPv4, with the transition from
32-bit coding of IPv4 addresses (4.3 billion addresses) to 128-bit
coding of IPv6 addresses (3.4 1038, or 340 billion, billion, billion,
billion addresses)for IPV6 the router needs to turn ON for whereas
IPV4 which is by default.
Simulation Setup
Packet tracer is the network simulator created by Cisco and
they provide the free distribution to student and faculty. It is
used to configure the routing protocols virtually and perform theoperations one by one and calculate the time travel for the
message from one node to another node. Starting phase network
model is design and secondary phase routing protocols been
configured. Packet tracer environment is shown below in Figure1.
Methodology Setup
In order to dig out the answers to the research questions,
the study adopted network model as the research strategy and
documents as data generation methods.
Network model
In the network model network topology been design in the
network simulator which basically consist of Router, Switch, cable
and End Nodes. In this work three different Network models were
design where configured these routing protocols one by one in
order to observe how theserouting protocols actually works. The
network model which is used to evaluate the time to travel the
packet from one end device(PC) to other end devices is shown
belowFigure 2.

Data collection
The research was carried out using ping techniques: which
is basically to check the connectivity to one node to other node
connected in different routing protocols RIP, EIGRP, OSPF and
network may be different so that packet can be send from source
to destination.as shown in Figure 3 a network model been design
for each routing protocols and calculate the time taken for the
packet to send and receive to the destination node. These data
were obtained while we run ping command from the traffic
generator and run the simulation using Auto/Capture/Play button
which show the time taken by the packet to travel from one station
to other station and finally reaching to the destination. These data
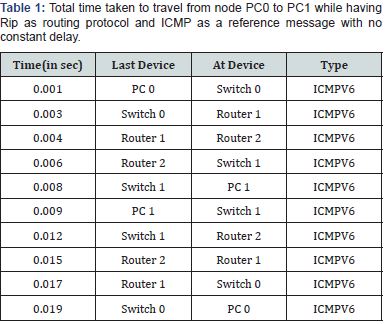
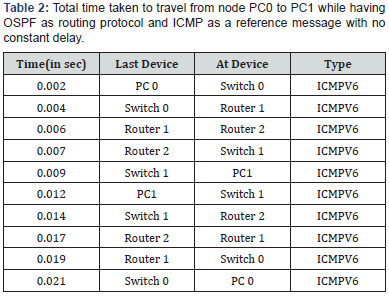
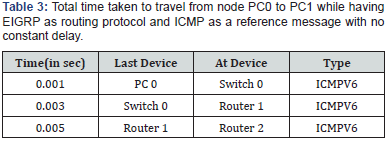
been noted down in Table 1-3with their respective station which
route the packet takes to reach the destination[5-10].
Data analysis
To measure and assess the impact of the traffic sent/received
in the network, the simulator was run under Best effort and traffic
generated through a ping method from PC0 to PC1 which show
the connectivity and transfer of packet from one node to other
and return the delivered message (reference Figure 2) varying the
simulation time with the observed parameters. Taking Figure 2
as a reference in ping method connectivity is checked from PC0
to PC1 from the network model which is done for each routing
protocols and have different time simulation from sending
and receiving packets done by the traffic generator and table is
constructed from the simulation time as shown in Tables1-3. And
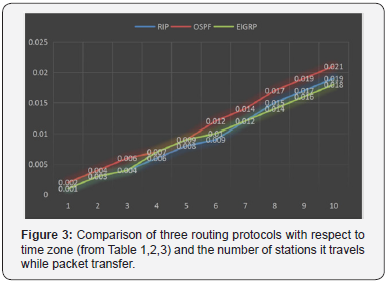
from each table a graph is constructed as shown in Figure 3and
finally reveled how these routing protocols performs.
Conclusion
Findings
The overall finding of the research provides the following result
1. The generated tableshow the different timezone(second)
in each station while traveling from one node to other node
with the path it follows that is the name of device where packet
take one station to check the destination address(Tables 1- 3).
2. Plot these generated timezone in a graph to
show the comparison between three different routing
protocols(RIP,EIGRP,OSPF). Which show EIGRP is
comparatively faster while other two protocols but in some
respect and small connection could lead to RIP faster.
3. IPV6 implemented in each routing protocols while IPV4
is outdated in some organization.
Contribution
My contribution in the field of computer networking while
working with these routing protocols are as follows:
1. Analysis of the time generated by each routing protocols.
2. Formulate the steps to calculate the evaluation of the
routing protocols on the basis of traffic generator
Limitation
Some limitations of this research can be summarized as
follows:
1. This research covers the small network as shown in
Figure2.
2. Although that is done on the simulator, but these values
could be difference in Router.
3. Among different routing protocols only three protocols
taken as major and evaluated.
4. As for IPV6 small number of nodes were define,where
nodes like PC0,PC1.
Recommendation for Future Work
The recommendations to the researchers for future work have
been listed below:
1. Researcher could include expand the research calculating
all the routing protocols in IPV6 which is currently running in
different organization.
2. Only conducted on PING traffic generator could extend
on different sector like HTTP,TELNET.
This paper demonstrated that CISCO Packet Tracer can be
employed by network planners to select the most suitable routing
protocol for various networks and to design an optimal routing
topology. Among RIP and OSPF routing protocols the best protocol
is EIGRP because it provides a better performance than RIP and
OSPF, it has a good impact in the world ofnetworking due to its
fast convergence time improved scalability and for sure the great
handling of routing loops and also EIGRP has a great impact in
PING application which gives it the power to be in the lead of
routing protocols.
For more articles in Open Access Journal of Engineering Technology please click on:
For more Open Access Journals please click on:




Comments
Post a Comment